About Us
Executive Editor:Publishing house "Academy of Natural History"
Editorial Board:
Asgarov S. (Azerbaijan), Alakbarov M. (Azerbaijan), Aliev Z. (Azerbaijan), Babayev N. (Uzbekistan), Chiladze G. (Georgia), Datskovsky I. (Israel), Garbuz I. (Moldova), Gleizer S. (Germany), Ershina A. (Kazakhstan), Kobzev D. (Switzerland), Kohl O. (Germany), Ktshanyan M. (Armenia), Lande D. (Ukraine), Ledvanov M. (Russia), Makats V. (Ukraine), Miletic L. (Serbia), Moskovkin V. (Ukraine), Murzagaliyeva A. (Kazakhstan), Novikov A. (Ukraine), Rahimov R. (Uzbekistan), Romanchuk A. (Ukraine), Shamshiev B. (Kyrgyzstan), Usheva M. (Bulgaria), Vasileva M. (Bulgar).
Middle class in the developed countries represents the main social group of populations (60-70%), including minor employers and high-paid hired workers, personal labour of which is a source of revenue. This class acts as a social stabilizer, inclined to support the state order existed, which has allowed to achieve their position [L. Grigoriyev et al., 2001]. In post-soviet Russia an overwhelming majority of people belongs to the lower social strata. Percentage of the population, ranked in the middle class, exceeds 10% a little. There is also a significant interlayer of «idealists», considering themselves among the middle class by their social-and-status orientation, which is not connected with the salary, proper for the middle class.
The base of the population differentiation in our country is a relation to MBG size, which changes from year to year, it is not the same in different regions, in different groups of population. The income below 0.5 MBG is poverty threshold, the income within the limits of MBG is determined as poverty level, families with the income up to 2 MBG - families of scanty means, with that of more 2-5 MBG - solvent families, with that 6-10-fold exceeding MBG - well-to-do families, and families with the income 100-fold exceeding MBG - wealthy families [N.D. Kremlev, 2007]. In 2006 the Kurgan region population with the income below 2 000 rubles amounted to 25%, below 4 000 rubles - 26.3%, below 7 000 rubles - 22.7%, and above 7 000 rubles - 30.9%.
The aim of the present study was to reveal the mean optimal level of Kurgan population incomes, which has the most favourable effect on the general condition and health of adult population, as well as on the health of newborns, and which allows to speak of a regional middle class.
METHOD OF STUDY
The main anthropometric, functional measurements and the welfare status in the families of women in labor (annually - not less than 100 persons at the age of 20-30 years, giving birth in June of every year in MI The Kurgan Town Hospital No. 2) within the period of 1989-2009, has been analyzed, as well as the anthropometric and functional measurements of newborns. Moreover, in 2009 the data of laboratory blood tests and the results of psycho-physiological testing quality of life have been analyzed using SF-36 questionnaire. The materials of study were analyzed statistically.
RESULTS OF STUDY AND THEIR DISCUSSION
It has been found, that the value of newborn functional maturity according to APGAR-1 scale, which amounted in Kurgan before 1990 to 7.84 ±0.07, by 1997 decreased to 7.21 ±0.10 (p≤0.001). In 2009 this value increased to 7.49 ±0.12. The dependence of the value on the income level of family members was analyzed on the basis of 2009 data (Fig. 1). The analysis has revealed inverse negative relationship between these values.
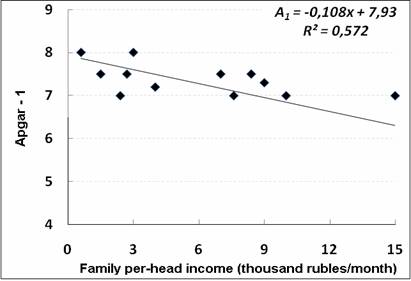
Figure 1. The dependence of the value of newborn functional maturity on the income level of women in labor families in 2009
Such a trend of the dynamics of newborn functional maturity value can be accounted for the known in biology principle of adaptation, according to which the periods of fetal maturation are shorter for more primitive individuals. Previously it was found that in girls, who were 5-9 years old in the period of Patriotic War, puberty was accelerated subsequently [B.A. Nikitiuk, 1978]. In women, who are going in for sport professionally, newborns have higher Apgar-1 values. This acceleration of fetal maturation does not further lead to the achievement of appropriate success in intellectual development [N.A. Abramovskikh et al., 2006].
Such conclusion was in part confirmed while analyzing the dynamics of Apgar-2 value. In children from families of scanty means the increment of Apgar-2 value after birth was slight. Nevertheless, the general regularity has been maintained: Apgar-2 value in newborns had a tendency towards decrease with income growth above the level of living wage (Fig. 2).
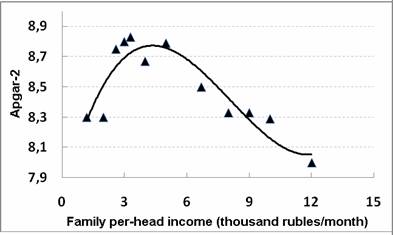
Figure 2. The dependence of Apgar-2 value on the income level of women in labor families
We have made the analysis of other values, which depend on the material well-being of women in labor. Body mass of women in labor has been to be the largest for the incomes, being at the level of minimal basket of goods. This phenomenon can be accounted for the compensatory increase of relatively cheaper products with more carbohydrate content (potatoes, flour and confectionery products) in their ration.
Women with the income at the level of minimal basket of goods (4.0÷0.5 thousand rubles per family member) had relatively smaller families in number and were subjected to induced abortion relatively more often (Table 1). The analysis of fetal palpitation rhythm revealed the higher level of the value in this group of women.
The value of somatic and gynecological diseases in number increased with the family income growth from 3 to 7 thousand rubles (Fig. 3). This value is not connected with the thoroughness of patients´ examination, because the matter concerns the women in labor, undergone standard examination. The decrease of chronic disease frequency was observed with further increase of incomes. Hemoglobin level was the highest in women with the income of 6-9 thousand rubles (Fig. 4). Percentage of complete families was the greatest in this group as well.
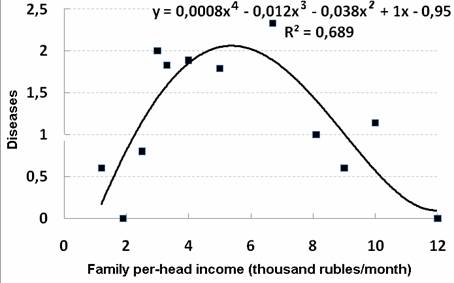
Figure 3. The dependence of diseases in number on the level of women´s income
Table 1. Some values of women in labor with different levels of family members´ income
|
Income level (thousand rubles) |
Family (members in number) |
Morbidity (chronic diseases in number) |
Abortions (in number) |
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) (points) |
Fetal palpitation (points) |
|
1.9÷0.3 |
3.7 ÷0.4 |
2.0 |
0.8÷ 0.3 |
51 ÷5 |
8.1 ÷0.3 |
|
4.0 ÷0.5 |
3.0 ÷0.2 |
2.3 |
1.9 ÷0.6 |
51 ÷1 |
9.1 ÷0.3 |
|
7.4÷0.5 |
3.2 ÷0.1 |
2.5 |
1.0 ÷0.3 |
50 ÷4 |
8.6 ÷0.3 |
|
10.8÷0.8 |
2.6 ÷0.2 |
2.2 |
1.0 ÷0.2 |
41 ÷6 |
8.5 ÷0.3 |
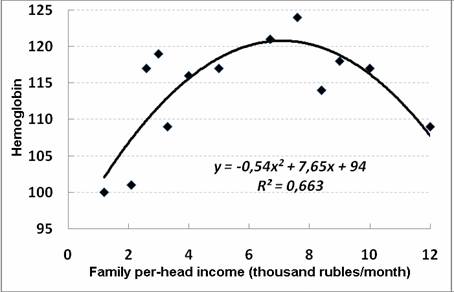
Figure 4. The dependence of mother´s blood hemoglobin level on women in labor well-being
The number of complete families decreased steadily for the last 20 years:
С = -0,0065x + 13,789; R² = 0,358.
The level of family well-being influenced this value not well enough, but the level of women´s education had a significant positive effect. The level of education was the highest for the incomes of 6-8 thousand rubles.
The size of external conjugate in women amounted to 19.9 ±0.1 cm I n 1990. The general tendency towards anatomic value increase is connected with continuing acceleration process. However, by 1997 this size decreased to 19.4 ±0.14 cm (p≤0.01), and in 2009 only it reached 20.3 ±0.10 cm (p≤0.001). Conjugate values depended on family incomes. They increased with income growth to 4-6 thousand rubles and remained at a stable level for further increase of well-being value (Fig. 5).
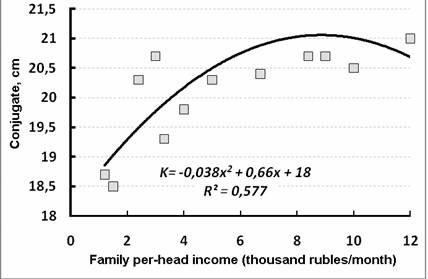
Figure 5. The relationship between external conjugate sizes and women in labor family incomes
The study of quality of life made in women in labor using SF-36 test has revealed that the total value increases rapidly with well-being growth up to the level of 8 thousand rubles per month, and it keeps at this level for further increase of incomes (Fig. 6).
According to Arndt-Schulz law, formulated in the 80s of XIV century, one and the same stimulus is able to have a different effect depending on dosage: weak stimuli excite vital processes, moderate ones increase them, and strong and very strong ones - suppress them. For example, it is known, that quite a number of environmental factors, causing organism growth inhibition, can have a stimulating effect on the organism in case of little degrees of influence [I.A. Arshavsky, 1963; P.G. Svetlov, 1978; F. Imms, 1967; D. Nash, 1968]. Material satisfaction of the most important living needs, in particular those for food, can be considered from the points of view of force relation law, from which it follows that the optimal level of consumption not at all conforms to that maximally possible.
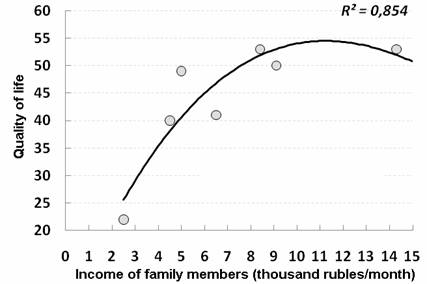
Figure 6. The dependence of the integral value of patients´ quality of life on the level of family incomes
It should be mentioned, that it´s impossible to define the level of optimal family incomes exactly by any parameter alone. The other thing is important: if unconditional minimum income exists, below which population´s quality of life becomes worse, there is a not so clearly designated corridor of well-being optimal values (7-10 thousand rubles per head), by which people may be related to the middle class, because in case of its excess some values have a tendency towards decrease. This optimal level of incomes is a reason to single out a middle class, which by its quantitative criteria is not comparative with the middle class of not only Western Europe countries, but with that of our capital centers. However, such singling out is justified, because it allows to remove an unreal infinity sign from the aim to achieve successful living standards.
This problem may be of practical importance as well. The experience of Western Europe countries in low birth rate stimulation by further improvement of families´ well-being level had no effect. Our observations have demonstrated that in families with low incomes the stimulation of generative activity occurs with well-being growth, and the rise of the number of abortions, but not labors, is a consequence of this stimulation. In the 50-th years of the past century the birth rate in the Kurgan region reached 45 per 1000 of population, in 1990 it decreased to 9 children. To find a way with the purpose of returning this value at least up to 1983 level (23 per 1000 of population) - this is the most important task of modern society.
REFERENCES
- Abramovskikh N.A., Shchurov V.A. Sportsmen children. Characteristic features of growth and development (in Russian) // Materialy yubilein. nauch.-prakt. konf. «Teoriya i praktika ozdorovleniya naselemiya Kurganskoi oblasti». Kurgan. 2006. P. 7-10.
- Arshavsky I.A. The problem of physiological immaturity and its significance in anthropology (in Russian) // Voprosy antropologii. 1963, Vyp. 15. P. 21-32.
- Grigoriyev L., Ivleva T. The middle class in Russia at the turn of transformation stages (in Russian) // Voprosy ekonomiki. 2001. No. 1.
- Nikitiuk B.A. The factors of organism growth and morphofunctional maturation (in Russian) // M.: Izd. Nauka. 1978. 144 p.
- Svetlov P.G. Physiology (mechanics) of development. Vol. 2. Internal and external developmental factors (in Russian). L., 1978. 261 p.
- Shchurov V.A., Kuznetsov A.P., Kholodkov V.A., ernal developmental factors. ian) // Voprosy ekonomiki. mulation of generative activity occurs with well-being g The effect of well-being on the growth, development of children and population health status (in Russian). Kurgan: Izd-vo Kurganskogo gos. Univesiteta. 2008. 170 p.
- Imms F. The effect of stress on growth rate and foоd and water inter intake of rats //J.Endocrinol. 1967. V. 37. N 1. P. 1-8.
- Nash D. F. Effects of radiation at weaning on growth of inbred and hybred mice. //Growth. 1968. V. 32. N 4. P. 297-310.
N. Mogeladze, V. Shchurov and V. Kholodkov FAMILY’S WELL-BEING LEVEL AND WOMEN’S HEALTH. International Journal Of Applied And Fundamental Research. – 2010. – № 4 –
URL: www.science-sd.com/386-23433 (15.12.2025).











 PDF
PDF